Union Territories (UTs) are administrative divisions in India that are ruled directly by the federal government, unlike states that have their own elected governments. The concept of Union Territories was introduced under the provisions of the Constitution of India.
The means or purpose of Union Territories is to provide direct administrative control of the central government over certain regions or territories for various reasons, such as strategic importance, effective governance, and better coordination between the central government and the local administration. Here are some key points regarding Union Territories:
1. Governance: Union Territories are administered by a Lieutenant Governor (LG) appointed by the President of India. The LG acts as the head of the administration and represents the President in the Union Territory.
2. Legislative Assembly: Some Union Territories have a Legislative Assembly, while others do not. Those with a Legislative Assembly are called "Legislative Assembly (L.A.)-based Union Territories" or "Partially/Partly L.A.-based Union Territories." The Legislative Assembly consists of elected representatives who have the power to make laws on certain matters.
3. Union Territory without Legislative Assembly: Union Territories without a Legislative Assembly are governed directly by the Lieutenant Governor and the President of India.
4. Special Status: Some Union Territories have been given special status or additional powers through specific constitutional amendments or acts, granting them more autonomy in certain areas of governance.
5. Administration: The central government, through its administrative departments and agencies, oversees various aspects of governance in Union Territories, including law and order, public services, infrastructure development, and fiscal management.
6. Representation: Union Territories are represented in the Parliament of India. They have representation in the Rajya Sabha (the Upper House) based on their population, and some Union Territories may also have representation in the Lok Sabha (the Lower House) if they have a Legislative Assembly.
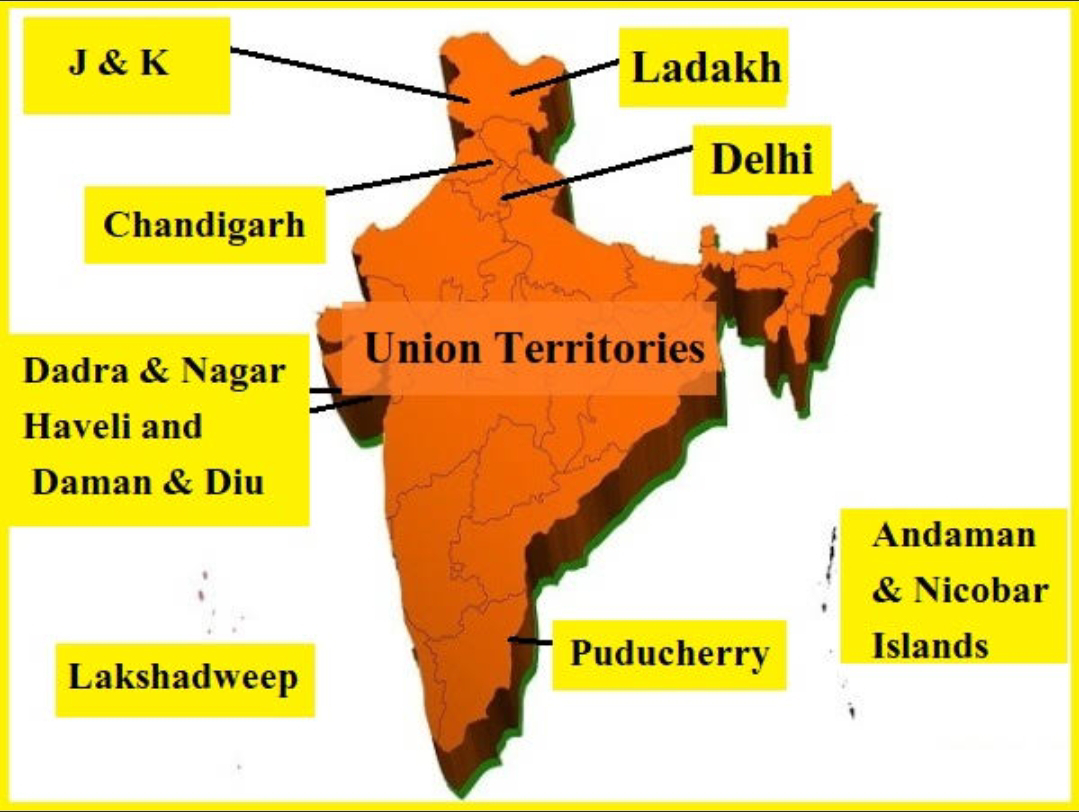
Examples of Union Territories in India include Delhi, Puducherry, Chandigarh, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Lakshadweep, and Ladakh.
It's worth noting that the status of Union Territories and their governance framework can be subject to changes and amendments by the central government based on evolving circumstances and requirements.
No comments:
Post a Comment