Beginning of World War II
It is said that on September 1, 1939, Germany attacked Poland, with which the Second World War began, after which England and France declared war on Germany, however, from September 1, 1939 to April 9, 1940. The war is called mock war because in this period a situation of war was created but no war took place during this period. On 9 April 1940, Germany invaded Norway and Denmark and occupied them.
By the end of June 1940, Belgium and Holland and France had also surrendered to Germany. After this, Germany wanted to capture England, but Germany could not capture England, however, in June 1941, Germany attacked the Soviet Union and captured a large area of the Soviet Union, but the Soviet Union, with the help of Moscow, defeated the Germans. attacked the army and forced it to return.
World War II (1939-1945) was a global conflict that involved many nations and had a profound impact on the course of history. Here's a brief overview of World War II:
Causes:
- The Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War I, imposed harsh terms on Germany and contributed to economic instability and resentment.
- The rise of totalitarian regimes, such as Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler and Fascist Italy under Benito Mussolini, fueled aggressive expansionist ambitions.
- Japan sought to establish dominance in East Asia and secure vital resources.
Key Events:
1. German Aggression:
- 1939: Germany invaded Poland, leading to the outbreak of war in Europe. Britain and France declared war on Germany.
- 1940: Germany launched the Blitzkrieg strategy, swiftly conquering Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France.
- 1940-1941: The Battle of Britain took place as Germany attempted to gain air superiority over Britain.
2. European Theater:
- 1941: Germany violated the non-aggression pact with the Soviet Union and launched a massive invasion.
- 1942-1943: Major battles such as Stalingrad and El Alamein turned the tide against the Axis powers.
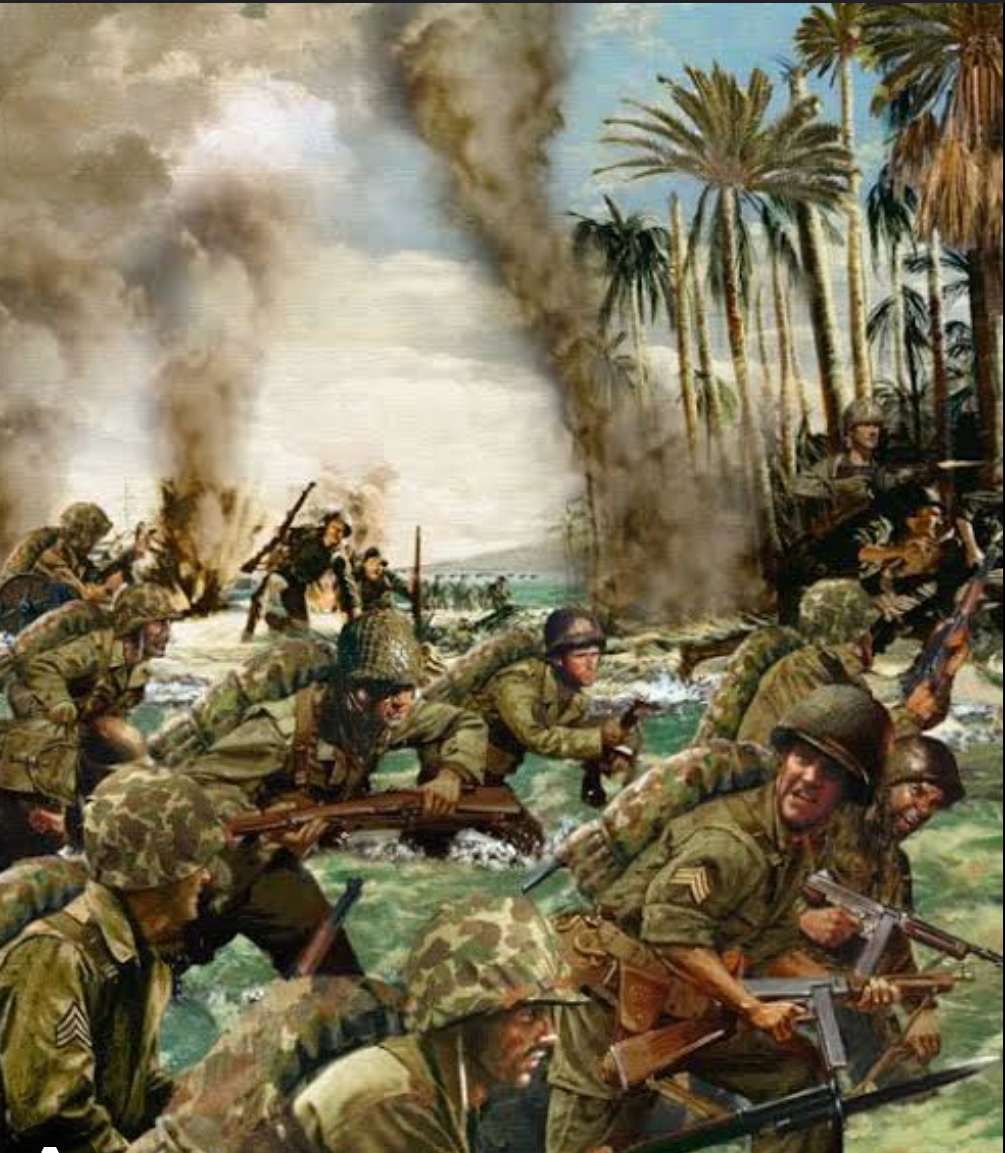
- 1944: D-Day, the Allied invasion of Normandy, marked a significant turning point in Europe. The Allies liberated France and advanced toward Germany.
3. Pacific Theater:
- 1941: Japan attacked the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor, prompting the United States to enter the war.
- 1942-1943: The Battle of Midway and the Guadalcanal campaign halted Japan's expansion in the Pacific.
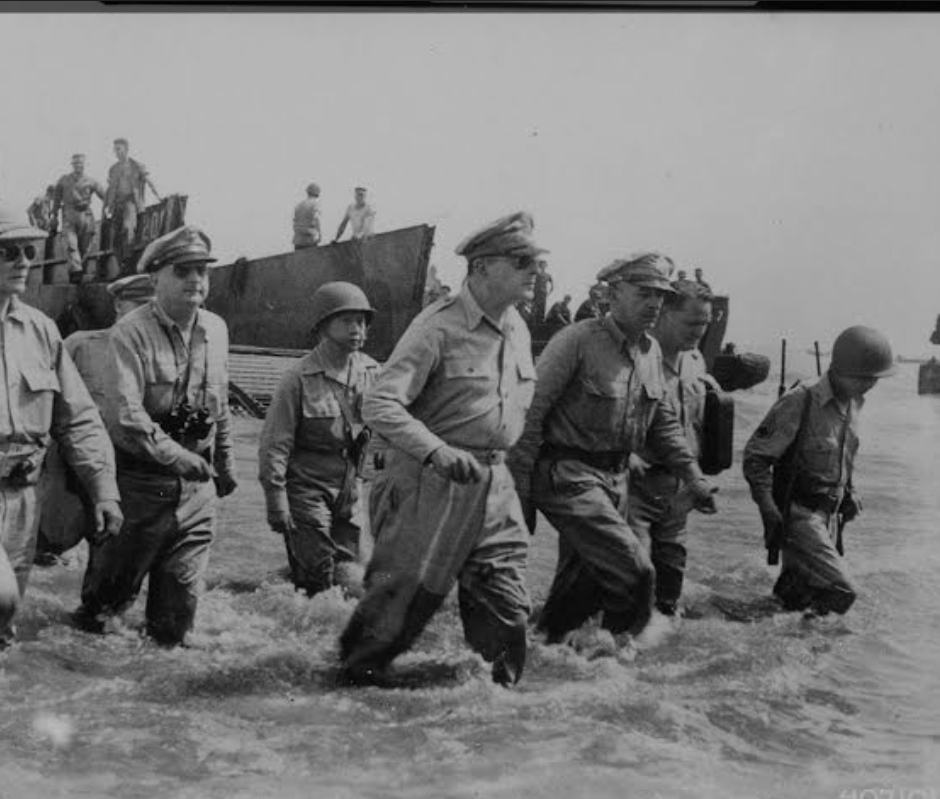
- 1944-1945: The Allies launched a series of island-hopping campaigns to retake strategic locations from Japan.
4. Holocaust and Genocide:
- The Holocaust, led by Nazi Germany, resulted in the systematic persecution and mass murder of approximately six million Jews, along with other groups considered undesirable by the Nazis.
5. Allied Victories:
- 1945: The Allies launched massive offensives on both the Eastern and Western fronts, leading to the fall of Berlin and the unconditional surrender of Germany in May.
- 1945: The United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, prompting Japan's surrender in August.
6. Aftermath:
- World War II left an estimated 70-85 million people dead, making it the deadliest conflict in human history.
- The war led to the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, shaping the Cold War.
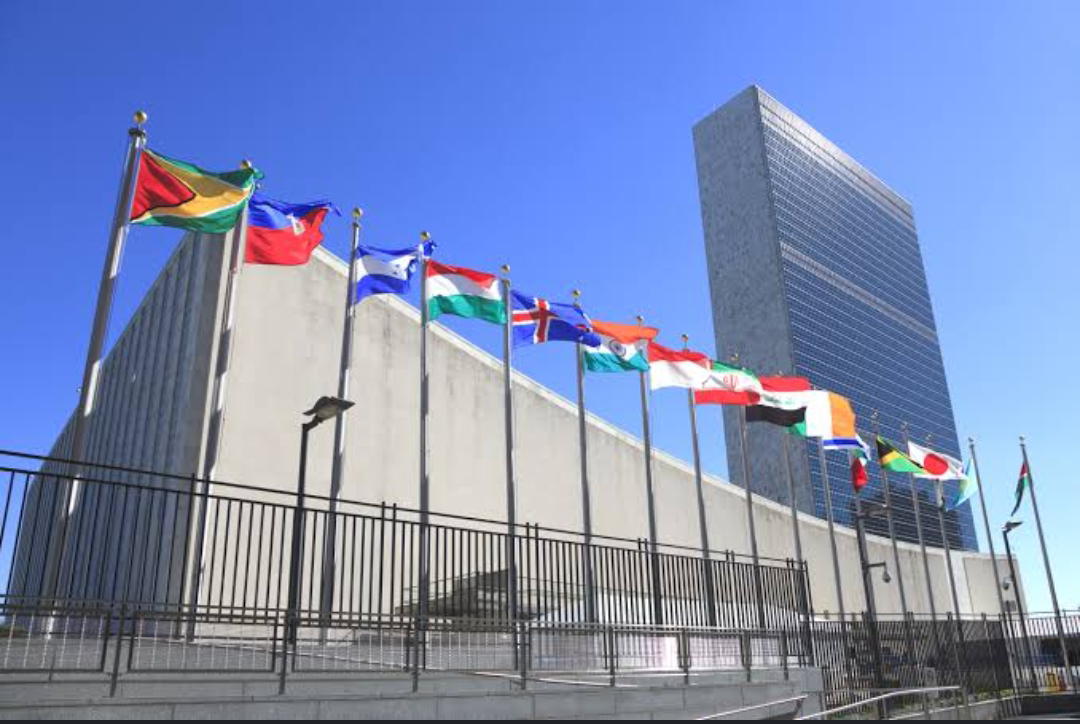
- The creation of the United Nations aimed to prevent future global conflicts.
The weak foreign policy based on appeasement adopted by Britain and France made World War II possible.
Countries Involved in World War II
During the First World War, the world was divided into two groups, the Allies and the Axis Powers, the Allied Powers included England, Japan, the United States of America, the Soviet Union (Russia) and France, and on the other hand, the Axis Powers included Germany, Italy, and Japan. were involved.
Army, Air Force and Navy of 70 countries took part in this war.
Result of World War II
1. Rise of new superpowers –
The situation of many countries and continents changed as a result of the Second World War. Before the Second World War, Britain and France were the two major superpowers of the world, but due to the World War, they lost their superpower status. As a result of the Second World War, the United States and The Soviet Union emerged as the two major superpowers of the world.
2. End of colonialism –
After the Second World War, Britain and France started grappling with various domestic and external problems. Both these countries were not able to control their colonies which resulted in the end of colonialism from Africa and Asia.
3. Establishment of United Nations –
As a result of the Second World War, the United Nations was established to establish peace among all the countries. The purpose of the establishment of the United Nations was to establish peace among the different countries of the world.
5. Beginning of the Cold War –
After the Second World War, a conference was organized in Potsdam, Germany to establish peace in the whole world, in this conference Germany was divided into four parts.
In these four parts, the first part was to be controlled by Britain, the second part by the United States, the third part by France and the fourth by the Soviet Union.
There were differences between the Western Allies and the Soviet Union on many things, as a result of which Germany was divided into East Germany and West Germany. Communist government was established in East Germany and democratic state in West Germany. This division of Germany led to Cold War. laid the foundation of
6. New World Economic Order -
As a result of World War II, the economic condition of many countries was very bad, many countries faced a worldwide economic crisis, a conference was organized to provide financial assistance to these countries, which is known as the Bretton Woods Conference.
The Bretton Woods Conference is also officially known as the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference. This conference was held from 1 July 1994 to 22 July 1944, in which representatives of 44 countries participated. The purpose of this conference was to provide assistance to the countries facing the worldwide crisis due to the Second World War.
World War II had a profound impact on geopolitical boundaries, the global balance of power, human rights, and the development of technology. Its consequences continue to shape the world today.